What is the magical triangle of learning?
Ever wondered why some training programs are successful, while not others? It has happened to most people: finishing a course, getting a certificate, but does not remember anything later. On the other hand, there are some training experiences that actually remain and implement what people learned for a long time. So, what’s the difference? All this is to do with it how a course is created. And the magic of learning this place comes.
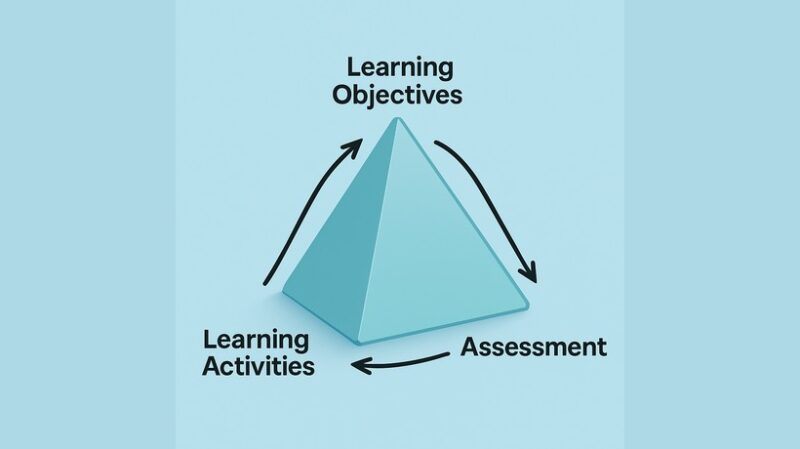
This framework connects three important elements that should have every effective learning experience: learning purposes, activities and diagnosis. When all three are attached, learning becomes clear, purpose and memorable. To make it more realized, make a picture of a triangle, arrows between each point. The goals form your activities, activities develop to learn the Learn for diagnosis, and the diagnosis shows whether your goals were met. The idea is in the teaching design, especially in the construction alignment, a term is popular by educational Theorest John Bugs. It is widely used in both educational settings and workplace training, and the reason is that it is effective. Let’s see how the magic triangle works, especially in the energing.
3 pillars of the magic triangle of learning
Pul 1: Learning goals
Learning goals are the secrets behind every well -designed course or training program. Without them, learners do not know where they are going, and teachers are at risk of creating courses that are not useful anywhere. Learning purposes are clear, measuring statements that highlight what learners should do by the end of the session or module. When developing your goals, try to use the active verb, such as “identify,” “create,” “apply,” or “analyze”. Also, focus on those who learn, as if they will do and not what you will teach them. Finally, always align them with wider goals, whether it be for a company, compliance, or a personal development plan.
Pillar 2: learning activities
Learning goals tell us what learners need to know or do, but the activities of learning are how they get there. They are hand -fired experiences that help to absorb, absorb and maintain new information in learning. These groups can be debates, interactive emission modules, case studies, role -playing exercises, or games. The point is to create opportunities where learners interact with information, not receive it. However, not all activities are the same. They are really effective, they need to be associated with your learning goals. For example, if your goal is to help someone handle conflicts at work, then the scene or imitation of playing more than the quiz is going to have a greater impact. You also need to keep in mind that different people can learn in different ways. Therefore, it helps everyone to be busy, including different types of activity, and the experience gives some meaningful.
Pul 3: Diagnosis
Therefore, you have designed clear learning goals and engaging activities. Now, how do you know that if all this was really effective? Through the diagnosis, which is the third pillar of the magic triangle of learning. Diagnosis are different, but in their basic part, they are the only tools to know if the learners have fulfilled your goals. There are two important types: formation and summary. Early diagnoses are like learning checkpoints, such as short quiz, debate indicators, or comments during activities. They help learners to stay on track. On the other hand, in the end, summary reviews such as final plans, offers, or skill demonstrations. This is more evidence of how effective it was to learn. Once again, the key to meaningful diagnosis is align. Your quiz, assignments, or tests should be linked directly to the scheduled goals.
What happens when 3 pillars are aligned?
So, what is actually when learning purposes, activities, and diagnosis are all straightforward? Learning becomes clear, purpose and effective. First, it encourages. Knowing what to do, how it is connected to the goals, and what happens to reach success makes it more confident in learning. They want to engage with this content because they know that it is relevant and plays a role in how they will be evaluated. The IT of teaching designers, it pushes the entire design process. When the goals are clear, choosing the right activities and designing the diagnosis that are really important.
What happens in case of misunderstanding?
Even if a piece of triangle is off, the best learning programs may fail. Unfortunately, this is often the case. One of the common problems is that when activities are disconnected from learning purposes. If learners cannot see how an activity helps them reach the purpose, engagement drops, and they don’t really learn. Then there are also reviews that were taught is not similar. This can be disappointing for learners. They can spend hours to learn a concept through videos and examples, only different different or theoretical. When the goals, activities and diagnosis are not synchronized, learners are confused. It feels unfair, and it’s not good to maintain.
How to put it into practice in Elming
Clear goals
To create clear purposes for your Elearning course, instead of ordinary goals, use statements that viable, measure, and allow no evidence. In this way, the learner knows exactly what is expected, and teaching designers know exactly what to build.
Meaningful activities
You need to be a bit more creative when designing meaningful activities. Instead of inactive methods, use interactive activities, such as slides, lectures, or videos, real -world compatible activities. For example, scenes where learners make decisions and see results, stories or imitation.
A meaningful diagnosis
Many elaring diagnosis only examine remembering knowledge, it is not applicable. But in the real world, learners must be able to work as they have learned. To make the diagnosis meaningful, ask if the test shows whether the learner can really fulfill the goal. For example, if the purpose is to learn how to run Google advertising campaigns, it would be more meaningful to assign them a project where they will run and run a joke.
The use of data and analytics
The biggest benefit of digital learning is data. You can see who the learners click, how much time they spend on each course, where they leave, and they often go wrong. But you need to learn how to use it. If you see that a specific activity is wrong for learners, see what you can do. Similarly, if a learner abandons a course or a particular part, try to make it more engaged.
Conclusion
Whether you are creating a university course, corporate training program, or online module, a magical triangle of learning can help keep you on the track. When your goals, activities and diagnoses are all synchronized, learning has the actual effect. Your learners are growing, promoting skills, and actually getting something they can use. Try to design the triangle, and you will see that you won’t do it in any other way.
