Solar and wind energy companies are betting a novel of insurance to protect their assets from the wild and volatility season.
Renewable power projects may lose enough income if the air fails to blow, if the clouds stop the sun, or when the hurricane is caught in the expensive infrastructure. Many, many owners, are turning to parameteric insurance, when some of the weather related measures are completed when the weather measures are completed. The negative side is that if the default trigger is also deprived of a small amount, there is no payment. And the amount paid can cover only a small part of the actual loss.
Nevertheless, more clean energy companies are using parametric insurance to complete traditional compensation programs. “This is definitely an area that we see widespread,” said Marseille-Stephen Reef, global weather chiefs and agriculture partners of the insurance company Munich RE.
Shift is running with the growing effects of global warming on green assets. In Texas, solar farms are normalized by the routine, while air farms are widely damaged during winter storms. Australia is watching the wind faster in some areas and the cloud cover in others. According to the Zuric Insurance Group AG, Europe’s renewable electricity capacity will be “extremely at risk” from the extreme weather unless nothing is done to protect them.
Read more: Disadvantages from the US Hurricanes can increase 50 % with global warming
Indonesia, Malaysia and Brunei have witnessed a huge decline in solar rays, and Qatar and Kuwait have seen a decrease in air speed in this century, according to Bloomberg -analyzed Coopernax climate change service data.
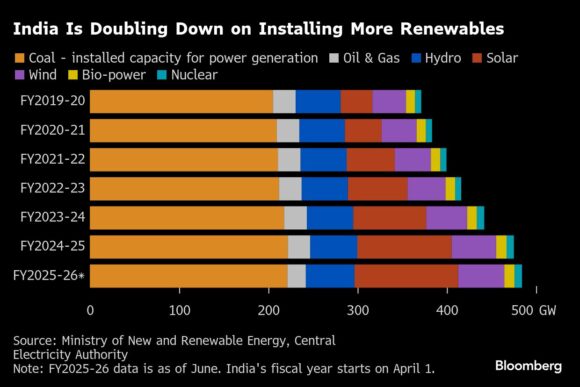
The threat is particularly severe in India, where Prime Minister Narendra Modi has damaged the country’s high sensitivity to reduce the drought and solar rays over double renewable energy capacity by 2030. According to a study of 2018 and 2018, wind power generation has decreased by 0.77 pitty hours per decade between 1980 and 2016, as the temperature on the Earth and the Indian Ocean’s Indian Ocean has less discrimination.
Such an unexpected capacity “increases the amount of equity needed for a project, which is obviously a hindrance to development, said Constitution Staff, a sustainable energy associate professor at Imperial College London.
A few years ago, the Energy Global PLC purchased parametric insurance for a minor size project, which tried to save revenue from a possible reduction in wind speed. But when he made any claim, the insurance refuses to pay, saying that the mistake was with a poor turbine rather than a variable weather. Renewal says the lack of payment discouraged it from buying parametric core for major projects.
“Wind has performed less in the last three to four years,” said Kailash Vaswani, chief financial officer of renewal, so that the insurance companies will have to significantly reduce the payment. “It’s basically the head in which they win, the tail loses to you.”
Some clean energy companies are worried about cost. Actis GPLP, who manages Billion 108 billion assets with parents’ general Atlantic, are talking to insurance companies, “to see if prices justify risk coverage,” said Abhishek, the Managing Director of Energy Infrastructure in Actis.
Read more: Destructive hedge fund strategy a hot new trend – parameters taps
However, foreign insurance seekers see a growing opportunity in emerging markets. Munich RE says it has received “first applications” from clean energy companies in India and China. Willis Towers Watson PLC says it has seen “double the demand” by the Indian developers since 2023. Discovering in Paris is undergoing air parameteric products in several developing countries.
The promise of sharp payments has become popular as hedge on parameteric deals, especially the hedge against the physiological effects of global warming – more sharp air breeze that eliminate solar panels, more frequently from power strikes that damage turbines. When Tophone Rai targeted the Philippines at the end of 2021, the Abu Dhabi Power Corporation succeeded in collecting a parameteric payment within 30 days and repairing the damage caused by its renewable energy assets.
“The most severe and more frequent weather events in the Asian region are more severe and more frequently in the Asian region,” said Jiong, a senior research fellow at the National University of Singapore. “Over time,” more and more parametric insurance products will be revealed to help cope with the risk of renewable sources, “he said.
Photo: March 20, 2024, Wind Turbines in Tamil Nadu, Tamil Nadu, Teroneville District, India. Photo Credit: Prashant Vishwanathan/Bloomberg
Copyright 2025 Bloomberg.
Titles
Climate change
Is interested Climate change?
Get automatic warnings for this title.
